Alcohol, tobacco, some medications, and recreational drugs are known to cause a host of health problems. Drinking alcohol to excess impacts more than just your liver. In fact, there are many ways in which misusing alcohol impacts oral health. The relation between alcohol and oral health and the effects of alcohol may vary based on the type of drink and the drinking frequency. These dental health problems often worsen overtime when heavy drinkers avoid dentist visits. Without treatment, tooth and gum damage can develop into serious diseases with serious consequences.
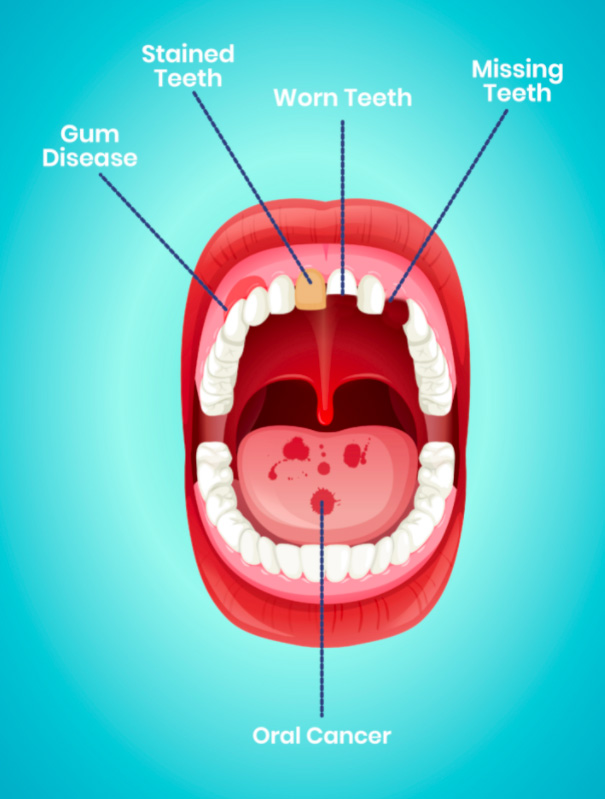
Alcohol And Oral Health
Oral Cancer
According to the Oral Cancer Foundation, “Alcohol abuse (when defined as more than 21 standard drinks in one week) is already the second largest risk factor for the development of oral cancer”. In fact, the Oral Health Foundation explains that 1 in 3 oral cancer cases is linked to excessive alcohol consumption. They explain that alcohol puts you at a higher risk for oral cancer when used with tobacco products. The alcohol helps harmful chemicals found in tobacco enter the cells that line the mouth and throat. The damaged cells try to repair themselves and cause DNA changes, which can ultimately lead to cancer. Ethanol is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic drinks such as beer, wine, and mixed drinks. “Overall, the amount of alcohol someone drinks over time, not the type of alcoholic beverage, seems to be the most important factor in raising cancer risk. Most evidence suggests that it is the ethanol that increases the risk, not other things in the drink” (The American Cancer Society).
Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
Periodontitis, or gum disease, is gum inflammation which can lead to tooth loss and heart and lung disease. Gum disease is characterized by red, swollen, and sensitive gums. The president of the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) explains why alcohol contributes to periodontal disease: “Alcohol slows the production of saliva, which helps neutralize the acids produced by plaque… An accumulation of these acids can lead to the early states of periodontal disease” (Dr. Joan Otomo-Corgel, DDS). Heavy drinkers will develop more plaque and bacteria which increase the risk of gum disease. In fact, in a study on 77 alcoholics, 69 individuals (89%) suffered from periodontitis. A study found that the connection between alcohol and increased periodontal disease was traced to bad oral hygiene and poor dental care.


Tooth Decay
The high acidity and sugar content in drinks such as beer, wine, and mixed drinks can cause tooth decay and cavities. The sugars and acids in these drinks break down enamel, which is the protective layer of the teeth. With continued alcohol abuse, the decay will continue and affect the pulp, or the soft inner layer of the teeth. Over time, this can lead to tooth pain, decay, and eventually tooth loss. According to Newmouth, “the condition is irreversible because enamel cannot regrow”. While enamel cannot be rebuilt or restored, damaged enamel can be remineralized using fluoride products.
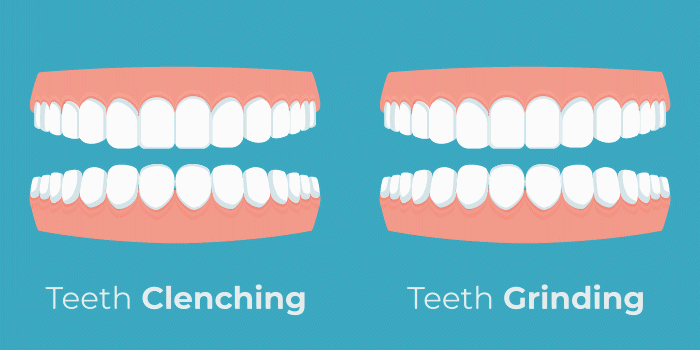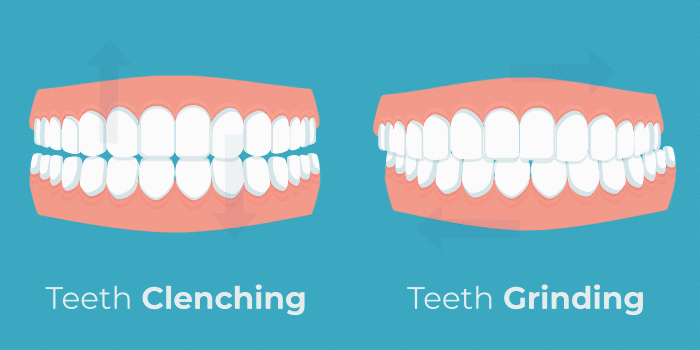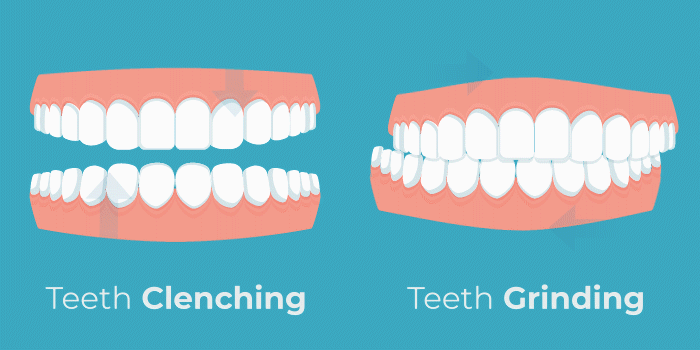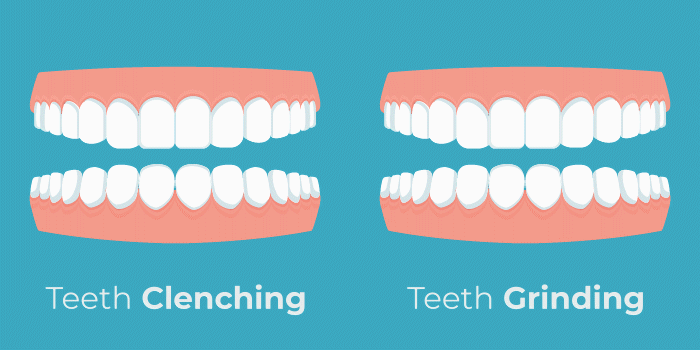
Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding and jaw clenching are referred to as a condition called bruxism. Alcohol has been linked to bruxism in recent research. A study conducted in 2016 found, “The odds for [sleep bruxism] seem to increase almost 2 times for those who drank alcohol”. Alcohol causes dehydration which can lead to grinding. Additionally, nocturnal bruxism occurs during light stages of sleep. Drinking alcohol before bed disrupts sleeping patterns, forcing you into these light stages of sleep, and allowing muscles to become hyperactive. This results in many painful symptoms including tooth sensitivity, jaw pain, neck pain, headaches, and even back pain.
Stained Teeth
Colored drinks or drinks with carbohydrates (sugars) cause staining of the teeth. Red wine and other drinks with a dark color will stain teeth and overtime create an overall dullness in color. In addition to colored drinks, sugary drinks stain teeth because they stick to the surface of the teeth and cause discoloration and erosion.
Dry Mouth
It is no secret that dehydration is a side effect of drinking alcohol. Dry mouth is a result of little or no saliva in the mouth. This can cause general discomfort in terms of chapped lips and sore throat. Additionally, dry mouth is associated with chronic bad breath. Overtime, lack of saliva can graduate from discomfort to pain and potentially dangerous oral problems such as tooth decay and mouth sores.
Related Articles:
How to Care for Your Oral Health
Alcohol clearly has many negative side effects on your oral health. If you suffer from these consequences of alcohol use, the best way to improve your oral health is to limit your alcohol intake. Some other ways you can improve your dental health include regular dentist visits and daily oral care such as brushing, flossing, etc. Fluoride products help protect the enamel on the teeth. Having regular dentist check ups is important as they can examine your teeth and mouth for signs of damage and recommend treatment options. Identifying the problem early is helpful to reverse tooth decay, gum disease, and damage from teeth grinding.
Sources:
- https://www.perio.org
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5535480/
- https://drugabuse.com/blog/tooth-and-consequences-alcohol-can-wreck-your-smile/
- https://www.newmouth.com/oral-health/effects/drug-addiction/
- https://oralcancerfoundation.org/understanding/alcohol-connection/
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-causes/diet-physical-activity/alcohol-use-and-cancer.html
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27522154/